What is green steel, and why is it important?
Meet companies and researchers working on making steel with renewable energy and fewer emissions.

Photo by ruhmal from Getty Images.
The process of making steel requires a lot of energy, which usually comes from fossil fuels. And it emits a lot of CO2. To be more sustainable, as well as for geopolitical reasons, we need to find ways to make steel using renewable energy sources and to reduce the amount of CO2 that is emitted. Such approaches are often called “green steel”.
Before we look at examples of green steel companies and R&D, let’s look at the difference between green and traditional steelmaking.
Traditional vs. green steelmaking technologies
Of course, all this is a lot more complicated. But key differences between “traditional” and “green” are (1) the fuel being used (fossil vs. renewable), and (2) the emissions (CO2 vs. water or oxygen).
Before I continue, an important caveat: I won’t talk about the entire steelmaking process below. Making steel includes making iron from iron ore, and then making steel from the iron. And below I will only talk about the “from iron ore to iron” part of the process.
Coke-based steelmaking
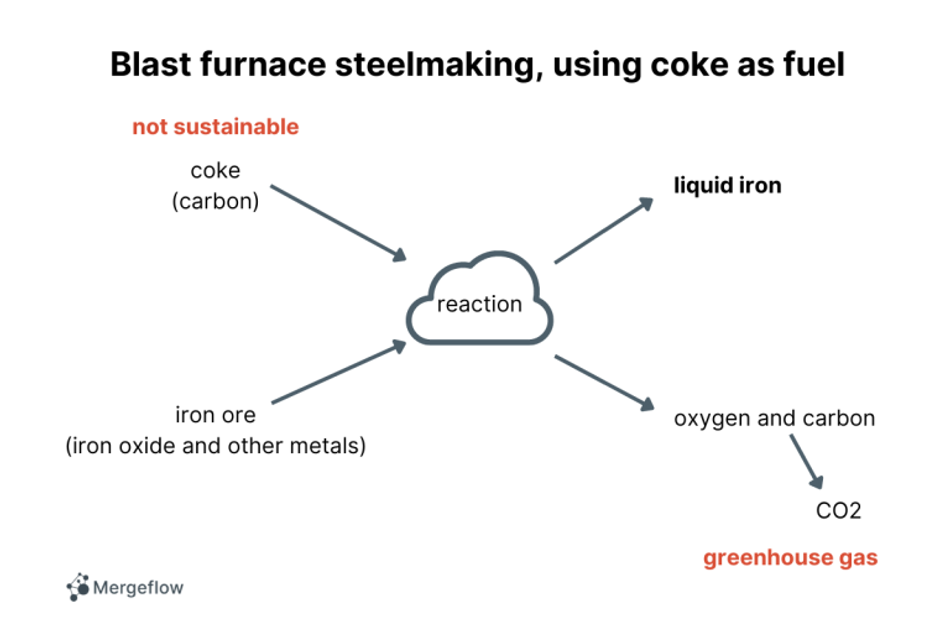
Traditional steelmaking often uses coke as fuel, in a process called blast furnace steelmaking. Coke is a coal-based material. In steelmaking, its purpose is to pull out the oxygen from iron ore.
Here is a very simple schematic of coke-based steelmaking (again, note that I left out the “liquid-iron-to-steel” steps of the process):
As you can see, blast furnace steelmaking uses non-sustainable fuel (the coke) and emits CO2. But we don’t want either if we can help it.
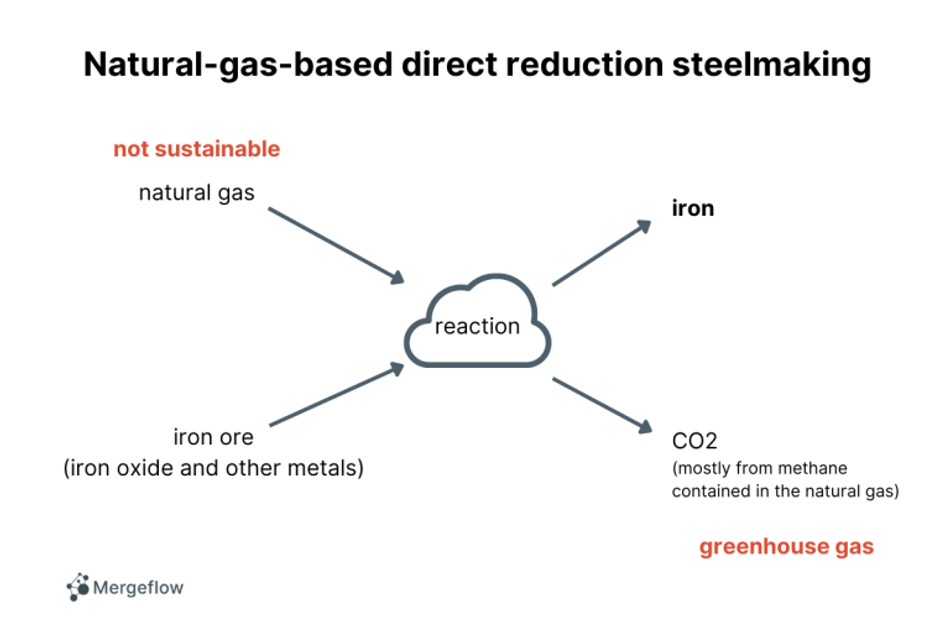
Direct-reduction-based steelmaking, using natural gas
Another method for steelmaking is called direct-reduction-based. This method uses natural gas as fuel, rather than coke:
This method has similar drawbacks to the coke-based method: The fuel is not sustainable, and it emits CO2.
A “green” version of direct reduction steelmaking
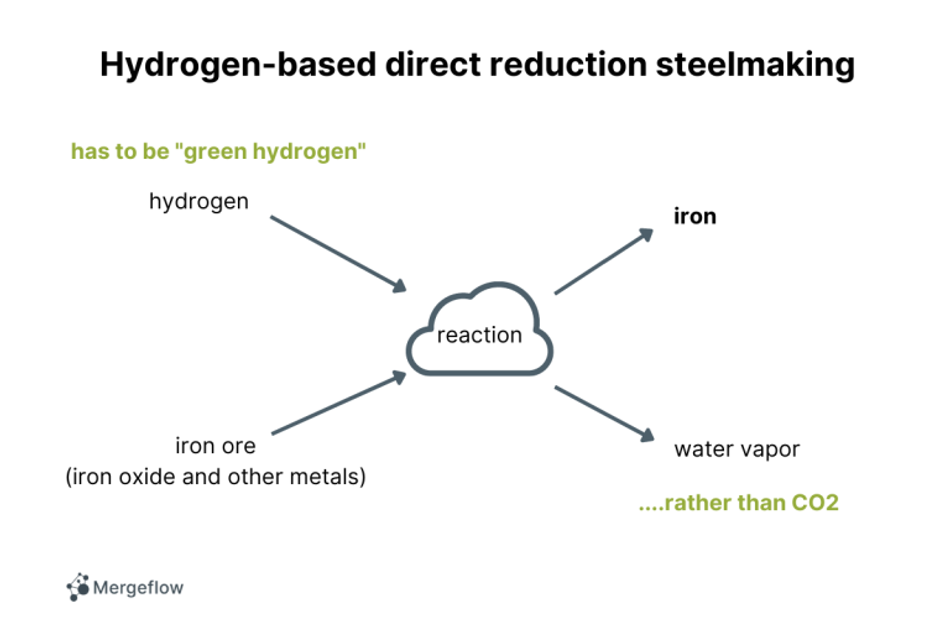
In order to get a “green” version of direct reduction steelmaking, you can use hydrogen as fuel, rather than natural gas:
Rather than natural gas, a more recent variant of direct reduction steelmaking uses hydrogen as fuel:
Rather than CO2, this method emits water vapor. And assuming that green hydrogen is used as fuel, then the fuel is sustainable as well.
Related article: Green hydrogen ventures and R&D
Swedish company SSAB is now beginning to use this method for making green steel. They collaborate with Volvo, and the plan is to start using the hydrogen-based steel for Volvo trucks in Q3 2022.

Other companies making green steel
Boston Metal: Building a new kind of green steel process
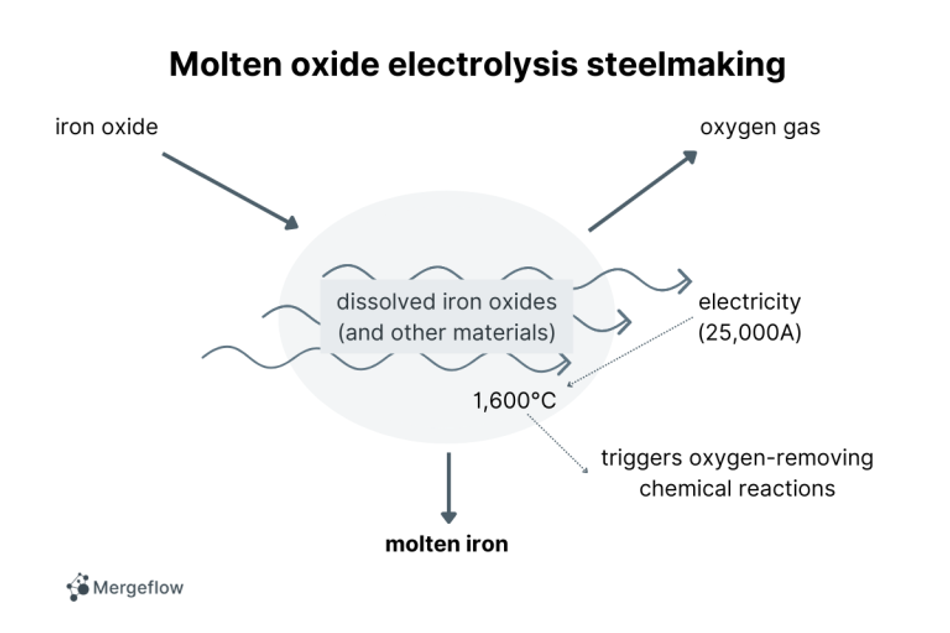
Boston Metal is a company that builds another steelmaking process, called molten oxide electrolysis. This process was developed by Donald Sadoway and Antoine Allanore at MIT. Here is a schematic of molten oxide electrolysis:
As you can see, this process requires electricity (which should be generated sustainably of course), and emits oxygen gas, rather than CO2.
I created a 360° data snapshot with Mergeflow that you can look at (requires no Mergeflow account):
Mergeflow 360° data snapshot on Boston Metal and molten oxide electrolysis ->
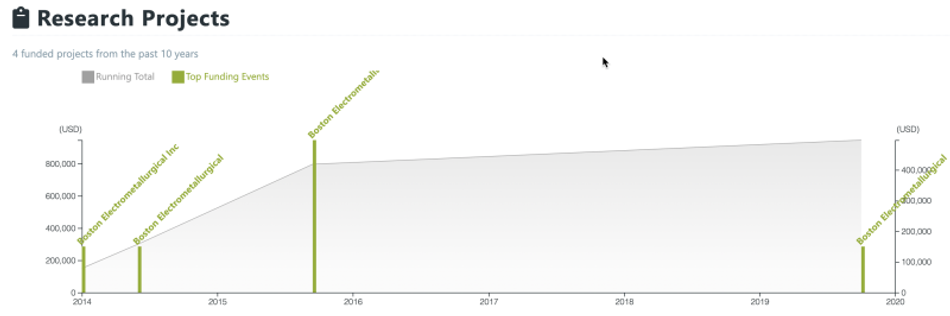
In this data snapshot you can see that Boston Metal has been around for quite some time (building new industrial processes is hard), and originally started out as Boston Electrometallurgical. Here is a screenshot with SBIR grants that Boston Electrometallurgical received:
More recently, in 2021, Boston Metal received $50M Series B funding from Piva Capital, BHP Ventures, Devonshire Investors, Breakthrough Energy Ventures, Prelude Ventures, OGCI Climate Investments, and The Engine.
Also, fun fact, according to this 2006 study by NASA (Donald Sadoway is a co-author), the molten oxide electrolysis process would even work on the Moon.
Midrex: Transitioning direct reduction steelmaking from natural gas to hydrogen
Midrex is a direct reduction steelmaking company. Currently their process runs with natural gas. According to Midrex, they currently produce more than 60% of all direct-reduction-based iron worldwide.
But while the Midrex process currently runs on natural gas, it can be gradually transitioned to using hydrogen. This means that you can mostly use current infrastructure, according to Midrex, which means reduced capital expenditure.
They are not just getting started. More than 20 years ago, Midrex patented a method for enriching natural gas with hydrogen:
Method and apparatus for producing reformed gases
And here is a more recent patent:
Direct reduction process utilizing hydrogen
If you have a Mergeflow account, you can explore more here:
Explore more Midrex patents related to hydrogen ->
If you don’t have a Mergeflow account yet, you can sign up for a free trial here.
H2 Green Steel
As the name implies, H2 Green Steel also works on using hydrogen to make steel production more sustainable. According to their website, the H2 Green Steel process is quite comprehensive. In addition to a direct-reduction-based iron ore process, they also make green hydrogen and produce the actual steel from the iron ore.
H2 Green Steel is a very young company, announced to the public only in 2021. At the time of this announcement, they mentioned “€2.5 billion of investment planned”. I could not find how much of this investment has actually closed. But investors mentioned include Spotify founder Daniel Ek, Scania, steel production equipment maker SMS Group, EU-funded EIT InnoEnergy, and Vargas Holding (who also invested in battery maker Northvolt).
Since 2021, H2 Green Steel has announced a number of supplier agreements (= agreements by which H2 Green Steel will supply steel to customers). This includes steel trader BE Group, BMW, Mercedes-Benz (also shareholder in H2GS), and automotive and industrial supplier Schaeffler.
As a buyer, H2 Green Steel partners with Hitachi Energy for electrical infrastructure and Iberdrola for renewable energy, for example.
See more news on H2 Green Steel ->
(the link above requires a Mergeflow account; if you don’t have one yet, you can sign up for a free trial here)
Recommended reading: Welding: What's new? And what does it have to do with going to the Moon?
Green steel R&D
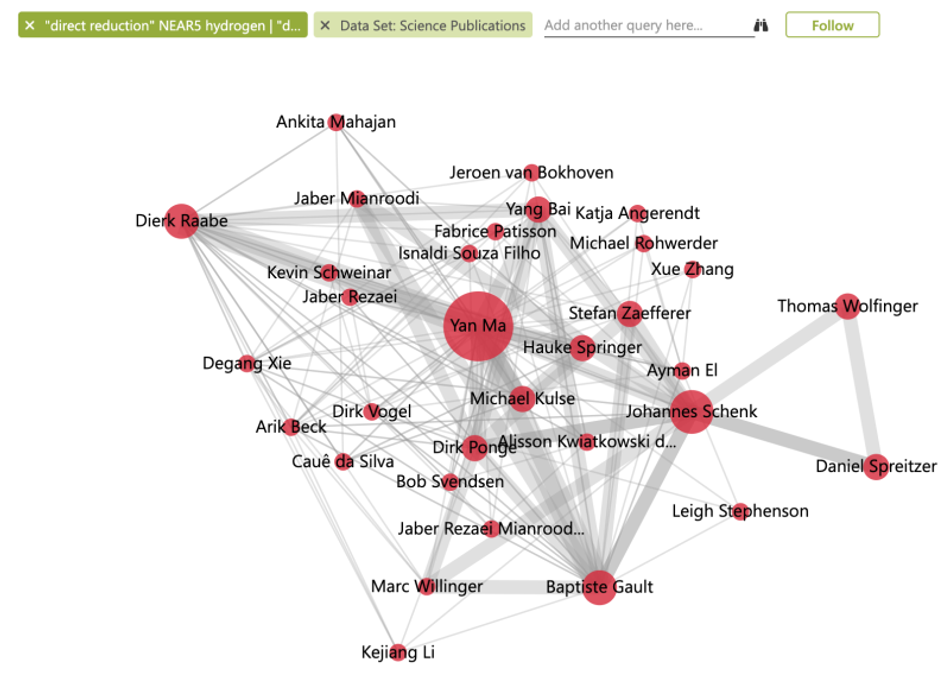
Rather than trying to be comprehensive, I’d like to point out one particular network of researchers in the green steel space.
Most researchers in this network work at the MPIE, the Max Planck Institute for Ferrous Metals Research (this is my translation of their name; they don’t translate “Max Planck Institute für Eisenforschung” into English anywhere). Below is a graph of the researcher network, generated by Mergeflow (“bigger circle” = “more publications”; “stronger connection” = “more co-publications”):
In Mergeflow, you can explore this network by clicking here. And for starters, here are some recent publications from the group (all hosted on arxiv.org, which means that you get the full text):
Green steel at its crossroads: hybrid hydrogen-based reduction of iron ores
Hierarchical nature of hydrogen-based direct reduction of iron oxides
Chemo-Mechanical Phase-Field Modeling of Iron Oxide Reduction with Hydrogen